Innate immune evasion revealed in a colorectal zebrafish xenograft model
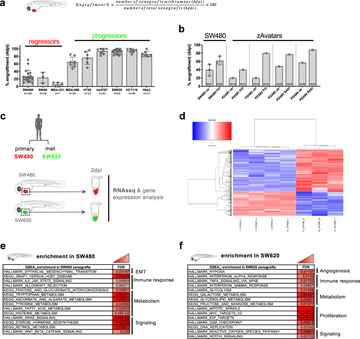
Cancer immunoediting is a dynamic process of crosstalk between tumor cells and the immune system. Herein, we explore the fast zebrafish xenograft model to investigate the innate immune contribution to this process. Using multiple breast and colorectal cancer cell lines and zAvatars, we find that some are cleared (regressors) while others engraft (progressors) in zebrafish xenografts. We focus on two human colorectal cancer cells derived from the same patient that show contrasting engraftment/clearance profiles. Using polyclonal xenografts to mimic intra-tumor heterogeneity, we demonstrate that SW620_progressors can block clearance of SW480_regressors. SW480_regressors recruit macrophages and neutrophils more efficiently than SW620_progressors; SW620_progressors however, modulate macrophages towards a pro-tumoral phenotype. Genetic and chemical suppression of myeloid cells indicates that macrophages and neutrophils play a crucial role in clearance. Single-cell-transcriptome analysis shows a fast subclonal selection, with clearance of regressor subclones associated with IFN/Notch signaling and escaper-expanded subclones with enrichment of IL10 pathway. Overall, our work opens the possibility of using zebrafish xenografts as living biomarkers of the tumor microenvironment (Povoa et al, Nature Communications, 2021).
Return to Research Highlights
